Quality Assurance Methods
Quality assurance (QA) is a systematic approach to ensuring that a product or service meets predefined standards and customer expectations. It’s an essential part of any industry, from manufacturing to software development, that helps businesses deliver high-quality outcomes. The primary goal of QA is to prevent defects in the design, production, and final delivery of products, ensuring customer satisfaction and long-term business success.

In this blog, we will explore various quality assurance methods and techniques used to maintain excellence across industries.
What is Quality Assurance?
Quality Assurance refers to the planned and systematic processes implemented to ensure that products and services are of consistent quality. Unlike Quality Control (QC), which focuses on identifying defects after they occur, QA is proactive, working to prevent defects from occurring in the first place. The goal is to implement efficient processes that yield reliable and high-quality results.
Why is Quality Assurance Important?
Quality assurance plays a vital role in ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations. Here are some of the key benefits of QA:
-
Customer Satisfaction: Consistent quality increases customer trust and satisfaction.
-
Cost Reduction: Identifying and preventing issues early can save significant costs on rework, returns, and wasted resources.
-
Compliance: QA ensures that products meet regulatory and industry standards, reducing the risk of legal issues.
-
Reputation: Delivering high-quality products enhances a company’s reputation and competitive edge.
Key Quality Assurance Methods
Several methodologies and tools are employed to achieve high standards of quality. Below are some of the most widely used quality assurance methods across various industries:
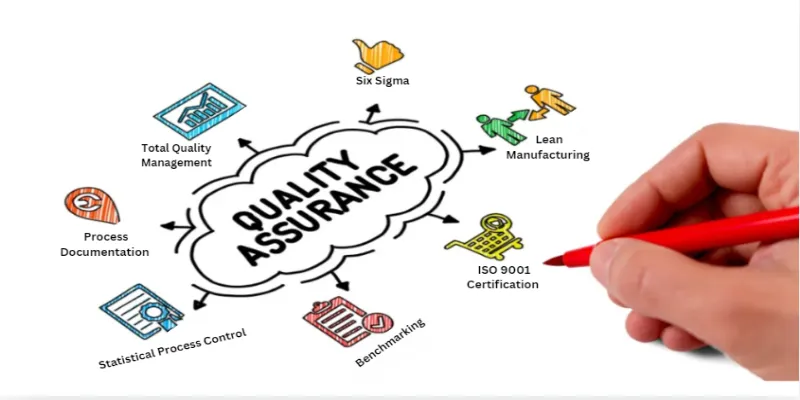
a. Process Documentation
One of the foundational methods in quality assurance is clear process documentation. Establishing written guidelines, procedures, and standards ensures that every team member understands the steps to maintain quality throughout the project or product lifecycle. It serves as a benchmark for evaluating performance and identifying areas of improvement.
b. Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is an organization-wide approach that focuses on continuous improvement of all processes, from production to customer service. The idea is to involve everyone in the company, from top management to line workers, in the pursuit of quality excellence. TQM is customer-focused and aims at long-term success through customer satisfaction.
Key components of TQM include:
- Continuous Improvement: Ongoing efforts to enhance products and processes.
- Employee Involvement: Empowering employees to participate in decision-making and improvement efforts.
- Customer Focus: Aligning products and services to customer needs.
c. Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven method that seeks to improve the quality of process outputs by identifying and eliminating the causes of defects and variability. This method aims for near perfection, with a goal of no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
Six Sigma uses two key methodologies:
- DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control – used to improve existing processes.
- DMADV: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify – used for creating new processes or products.
d. Lean Manufacturing
Lean focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing productivity. It aims to streamline processes by eliminating activities that do not add value to the customer. Lean methods encourage efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure higher quality output by focusing on continuous improvement.
Lean uses tools such as:
- 5S Methodology: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain – a workplace organization method.
- Kaizen: Continuous improvement involving all employees.
e. ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized quality management standard. Companies that achieve ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to maintaining high-quality processes and products. The ISO 9001 standard sets out the criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and is based on principles such as customer focus, leadership, process approach, and continuous improvement.
f. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing your company’s processes, products, or services with the best in the industry. By identifying gaps in performance and adopting best practices, organizations can improve their quality standards and achieve better outcomes. Benchmarking helps businesses identify areas where they lag and where improvements can be made.
g. Statistical Process Control (SPC)
SPC is a method of quality control that uses statistical tools to monitor and control processes. By collecting data in real-time, organizations can identify variations and trends that may indicate potential problems. This allows for adjustments before defects occur, ensuring consistent quality output.
Key tools used in SPC include:
- Control Charts: Graphical tools that monitor process performance.
- Pareto Analysis: A method to identify the most significant causes of defects or issues.
Tools and Techniques for Effective QA
In addition to methodologies, quality assurance relies on a variety of tools and techniques that help businesses measure, monitor, and improve quality. Some of the most popular QA tools include:

-
Checklists: Simple yet effective for ensuring all steps in a process are completed correctly.
-
Fishbone Diagram : (Cause-and-Effect Diagram): Identifies the root causes of defects or problems.
-
Flowcharts: Visual representations of processes that help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
-
Histogram: A graphical tool that represents data distribution and helps identify patterns in process outcomes.
The Role of Quality Control in QA
While quality assurance is focused on preventing defects, quality control (QC) plays a crucial role in detecting them. QA and QC work hand-in-hand to ensure that products meet the desired quality standards. QC involves inspecting and testing products at various stages of production to catch any defects that may have slipped through. Together, QA and QC form a comprehensive quality management strategy that ensures products meet customer expectations.
The Future of Quality Assurance: Automation and AI
As technology advances, automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are becoming increasingly integrated into quality assurance processes. Automated testing tools are helping organizations streamline QA tasks, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. AI-driven systems can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict potential quality issues before they arise.
By leveraging these advanced technologies, businesses can maintain high-quality standards while improving productivity and reducing operational costs.
Quality Assurance Excellence with AMREP Mexico
Quality assurance is an integral part of any business process that strives for excellence. By implementing structured QA methods businesses will see long-term success and customer satisfaction. Investing in quality assurance is not just about delivering great products—it’s about building a reputation for reliability and excellence that will set your business apart from the competition.
By adopting different QA methods and tools, your organization can ensure a high level of quality across all its processes, driving success and growth in the long term.
At AMREP Mexico, we specialize in providing best quality assurance services designed to your unique business needs. With our experienced team and commitment to delivering exceptional results, we help you maintain the highest standards of quality across all your processes. Contact us today to learn how we can support your business in achieving consistent excellence.


