Quality Control in Healthcare: Ensuring Safe and Effective Care
Quality control in healthcare is crucial for providing safe, efficient, and effective care to patients. It ensures that medical services meet the highest standards. Through systematic processes, healthcare organizations improve the overall experience for patients and reduce the risk of errors.

What is Quality Control in Healthcare?
Quality control in healthcare refers to a set of practices aimed at maintaining and improving the quality of care delivered to patients. It involves monitoring and evaluating healthcare services, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing solutions.
Quality control improves patient outcomes. It ensures treatments are effective, and healthcare providers follow the right procedures. By focusing on quality, healthcare providers reduce mistakes, minimize complications, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Components of Quality Control
The components of quality control are designed to prevent defects, improve efficiency, and optimize overall performance. Below are the fundamental components of quality control:
- Standardized Procedures: Consistency is key in healthcare. Standardized procedures help ensure that treatments and practices are reliable and efficient.
- Patient Safety: One of the main goals of quality control is to protect patients from harm. This includes reducing hospital-acquired infections, medication errors, and surgical complications.
- Performance Monitoring: Regular assessment of healthcare staff performance helps identify strengths and areas that need improvement. This ensures continuous growth and better service delivery.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Healthcare providers rely on data to track progress, make informed decisions, and improve patient care. From patient feedback to medical records, data helps pinpoint issues and optimize care.
- Staff Training and Education: Ongoing training is essential to keep staff updated on the latest medical practices and technologies. Well-trained professionals are more likely to deliver higher-quality care.
Challenges in Quality Control
Quality control is essential for ensuring that products and services meet the desired standards. However, achieving consistent quality can be challenging. Companies often face several obstacles that hinder the smooth implementation of quality control processes. Below are some of the key challenges in quality control:
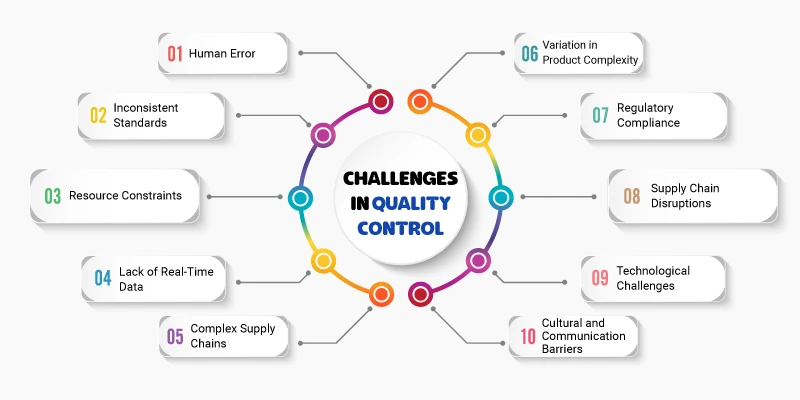
1. Human Error
One of the most common challenges in quality control is human error. Even the most experienced workers can make mistakes during inspections, measurements, or assessments. These errors can lead to faulty products, delayed shipments, and compromised customer satisfaction. To mitigate this, businesses must invest in training and automation to reduce human involvement in critical quality control tasks.
2. Inconsistent Standards
Maintaining consistent quality standards across multiple production lines, locations, or suppliers can be difficult. Different suppliers may have varying quality practices or materials, which can result in inconsistencies in the final product. Standardizing procedures and enforcing strict guidelines across the entire supply chain can help address this challenge.
3. Resource Constraints
Quality control often requires significant resources, including time, labor, and technology. Small businesses or those with limited budgets may struggle to invest in advanced quality control tools, testing equipment, or skilled personnel. This can lead to slower quality checks, less accurate inspections, or even skipped quality control steps, which can negatively impact product reliability.
4. Lack of Real-Time Data
Many companies still rely on traditional, manual methods of data collection and analysis for quality control. This approach can be slow and error-prone. The absence of real-time data makes it difficult to spot issues early in the production process, leading to delays and increased costs. Implementing digital tools, sensors, and data analytics systems can address this challenge by providing real-time insights into product quality.
5. Complex Supply Chains
Global supply chains can create significant challenges for quality control. Products often pass through multiple suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors before reaching customers. This complexity makes it difficult to monitor and ensure the quality of every part or material used in the final product. Strengthening communication with suppliers and using technology to track the movement and quality of materials can help mitigate this issue.
6. Variation in Product Complexity
As products become more complex, the difficulty in maintaining consistent quality increases. Multi-component products or those with advanced technologies may require intricate and time-consuming testing and inspections. Managing quality control for these complex products demands highly specialized equipment, trained staff, and more rigorous testing procedures.
7. Regulatory Compliance
Companies in regulated industries, such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, and food production, face the added challenge of complying with strict industry standards and regulations. Failing to meet regulatory requirements can lead to costly recalls, fines, or damage to a company’s reputation. Adhering to these standards requires constant monitoring, training, and updates to quality control practices.
8. Supply Chain Disruptions
Events like natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or sudden changes in demand can disrupt the supply chain, making it difficult to maintain consistent quality. When suppliers are unable to meet quality standards or delivery timelines, businesses must adapt quickly to ensure that quality isn’t compromised. This often involves having contingency plans and maintaining good relationships with alternate suppliers.
9. Technological Challenges
While technology has a critical role in improving quality control, integrating new systems can be challenging. Companies may struggle with selecting the right technology, training employees, and ensuring that the new systems are fully integrated with existing processes. Moreover, the cost of high-end quality control technologies may be prohibitive for some businesses.
10. Cultural and Communication Barriers
In global companies, differences in work culture, language, and communication styles can create challenges in maintaining quality standards. Teams working in different locations may have different approaches to quality control, leading to inconsistencies. Establishing a culture of quality, promoting clear communication, and regular training are key to overcoming these barriers.
Read More: Quality Control in Aerospace Industry
The Role of Technology in Quality Control
Technology has become a cornerstone in modern quality control, revolutionizing the way industries ensure that products and services meet required standards. From manufacturing to healthcare, technology plays a pivotal role in increasing efficiency, precision, and consistency in quality management. Here's a breakdown of how technology influences and improves quality control:
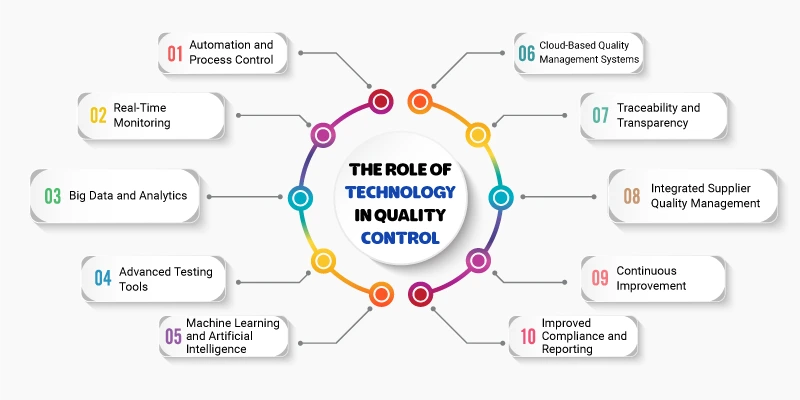
1. Automation and Process Control
Automation tools are essential for reducing human error in quality control processes. Machines and robots can perform repetitive tasks with higher consistency and speed than manual labor. For instance, automated inspection systems can quickly detect defects in products during production, ensuring they meet specifications without human intervention. This not only improves quality but also reduces labor costs and increases productivity.
2. Real-Time MonitoringKey Benefits of Quality Control
Technology allows businesses to monitor production lines in real time, providing immediate feedback about quality deviations. Using systems like SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition), companies can track every stage of production, ensuring that any variations are detected instantly. Real-time data enables quick corrective actions, preventing defects from progressing further down the production line.
3. Big Data and Analytics
With the help of Big Data, quality control now involves analyzing vast amounts of data generated from production processes. These analytics tools can identify patterns, detect potential issues early, and suggest improvements. Predictive analytics, powered by artificial intelligence (AI), can anticipate quality problems before they arise, enabling proactive interventions to maintain high-quality standards.
4. Advanced Testing Tools
Technological advancements have introduced more precise and accurate testing tools that improve the reliability of quality control. In manufacturing, tools like 3D scanners, ultrasonic sensors, and X-ray machines are used to inspect product integrity without damaging them. These tools can detect microscopic flaws or internal defects that might not be visible to the naked eye, ensuring a higher level of product quality.
5. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
AI and machine learning algorithms enhance quality control by learning from historical data and continuously improving their accuracy. For example, AI can be used in visual inspection systems to automatically identify defects, imperfections, or inconsistencies in products, surpassing human capabilities. The more data these systems process, the more accurate they become, reducing false positives and ensuring better quality assurance.
6. Cloud-Based Quality Management Systems (QMS)
Cloud-based Quality Management Systems (QMS) help organizations manage quality control processes efficiently. These systems centralize quality data, making it easily accessible to stakeholders in real time. They provide tools for documentation, tracking, and reporting, which help ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. Cloud-based systems also support collaboration across different teams and locations, improving communication and decision-making in quality management.
7. Traceability and Transparency
With the integration of technologies like blockchain and IoT (Internet of Things), companies can ensure traceability and transparency in their supply chains. Blockchain allows for secure, immutable records of every stage a product goes through, from raw material sourcing to production and delivery. IoT devices, such as RFID tags, can monitor and record the conditions of products in transit, ensuring that the items maintain quality from start to finish.
8. Integrated Supplier Quality Management
Technology allows companies to better manage relationships with suppliers by monitoring their performance and quality metrics. Supplier performance management tools can assess how suppliers meet the required standards, track quality data, and ensure that raw materials or components meet specifications before they enter production. This reduces the risk of receiving substandard materials that could affect the final product’s quality.
9. Continuous Improvement
Technology plays a key role in the continuous improvement process. Tools like Six Sigma, Kaizen, and Total Quality Management (TQM) can be integrated with software platforms to help organizations identify inefficiencies, reduce defects, and enhance overall performance. These systems provide data-driven insights that support continuous quality improvement initiatives and foster a culture of excellence within the organization.
10. Improved Compliance and Reporting
With regulatory standards becoming more stringent, technology helps businesses stay compliant by automating reporting and documentation processes. Regulatory bodies often require detailed records of quality control activities, and technology ensures that these records are accurate and up to date. By using automated systems for compliance tracking, companies can ensure that they meet industry regulations without the risk of human error.
Also Read: Quality Control in Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
Supplier Quality Services at AMREP Mexico
At AMREP Mexico, we understand the critical role that Supplier Quality services play in delivering exceptional healthcare outcomes. Our commitment to rigorous supplier evaluation processes helps us maintain consistency in our offerings and reduces any risks associated with subpar products or services. With AMREP Mexico's dedicated focus on Supplier Quality services, we strengthen our ability to provide top-tier care to patients, while fostering long-term, mutually beneficial partnerships with our suppliers. This focus on quality is a cornerstone of our overall mission to enhance healthcare through continuous improvement and innovation.